Classified as a mental disorder, schizophrenia is usually characterized by abnormal behavioral patterns and an inability to distinguish fact from fiction. Confused thinking, hallucinations and a lack of interest in social activities are among the symptoms most often displayed by schizophrenia patients.
Although the condition has been known to the medical community for quite a while, since the early 20th century, the fact of the matter is not much is explained about schizophrenia. For one thing, scientists are yet to determine exactly what causes it.
Inflammation in the brain appears to be involved
In a study published earlier this week in the American Journal of Psychiatry, researchers at Imperial College London propose that, as shown by their investigations into the matter at hand, there is a link between inflammation in the brain and this mental disorder.
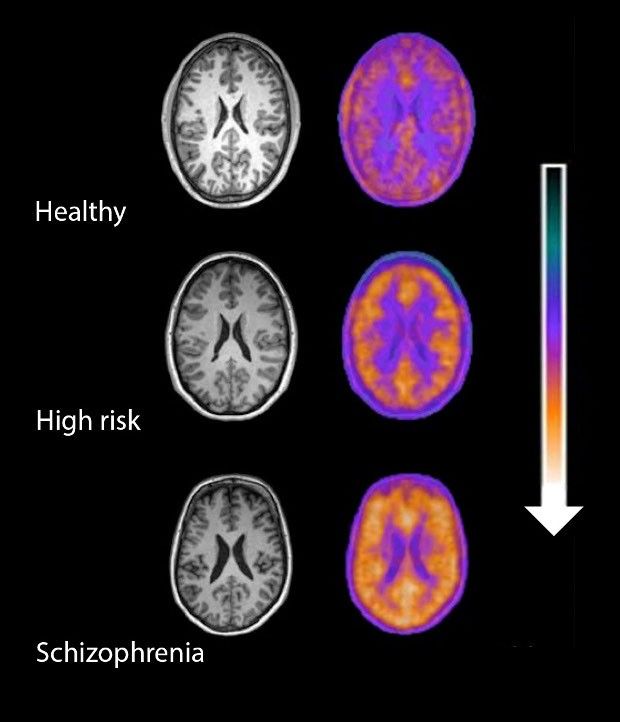
The scientists explain how, having studied the brains of several people who risk developing schizophrenia and actual schizophrenia patients, they documented an increase in immune activity.
More precisely, they detected increased levels of activity of microglia, which are special cells of the immune system designed to fight damage and infections. In some cases, these cells are known to rearrange connections between brain cells to optimize their work.
Interestingly, the Imperial College London research team found that, the more severe schizophrenia symptoms a patient displayed, the more active the microglia populating their brain were.
“Activity levels of microglia in the brain increased according to the severity of symptoms in people with schizophrenia,” the scientists write in a report detailing their work. “Immune cells are more active in the brains of people at risk of schizophrenia,” they further detail.
So, what does this find tell us about schizophrenia?
For one thing, the scientists behind this investigation explain that this increased immune activity in the brain of schizophrenia patients and people most at risk of developing this mental disorder hints that the disease correlates with inflammation.
Then, the specialists argue that, now that this correlation has at long last been documented, it might be possible to use this piece of information to identify people who are at risk before they progress to developing the disease. These people could be administered drugs to reduce inflammation in the brain in the hope that this might delay, maybe even halt the onset of the disease.
“This is a promising study as it suggests that inflammation may lead to schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. We now aim to test whether anti-inflammatory treatments can target these,” said researcher Oliver Howes in an interview.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //