The imitation game is not only the name of a Hollywood film about the life of Alan Turing, played by Benedict Cumberbatch, but also a daily way of doing business for some ransomware operators.
According to a Trend Micro report, there's a ransomware family going around these days trying to pass as CryptXXX, a much more deadly variant that's one of the top three most encountered ransomware families in the past month, according to a Microsoft report.
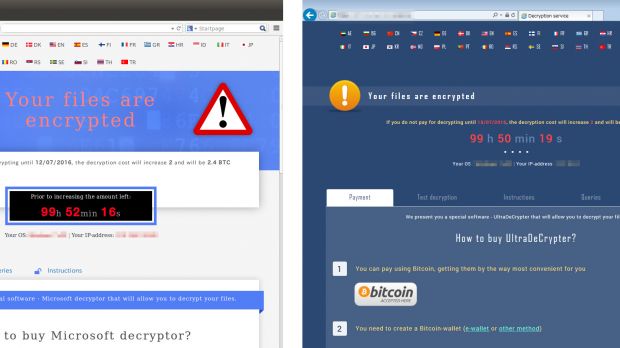
Named CryptMIC, this threat mimics CryptXXX to perfection. It uses the same ransom notes, the same UI for the ransom payment site, the same distribution methods (Neutrino exploit kit via malvertising, compromised websites), the same ransom sum demand, a custom C&C server communications protocol, and even employs the same structure to generate the individual IDs for infected victims.
Why, you might ask? The answer is simple. If victims think they were infected by one of today's most powerful and deadly ransomware families, they would be inclined to pay the ransom without waiting.
Not a perfect clone, but close
Nonetheless, CryptMIC is not a perfect copy of CryptXXX. It still lacks CryptXXX's more powerful encryption routine, the ability to infect and encrypt unmapped network drives, lockscreen capabilities, and password-stealing functions.
CrytMIC is not the only ransomware variant that plays the imitation game. Also this week, security researchers were able to create a decrypter to unlock files encrypted by the PowerWare ransomware, which was imitating Locky and had previously copied TeslaCrypt and CryptoWall.
Below is a table that compares CryptMIC and CryptXXX capabilities in greater detail.
| CrypMIC | CryptXXX 4.001 / 5.001 | |
|---|---|---|
| Attack Vectors | Malvertising, compromised websites | Malvertising, compromised websites |
| Exploit Kit | Neutrino | Neutrino |
| File Name and Type | Randomly named DLL file (rad{randomhexcharacters}.tmp.dll when dropped by Neutrino) | Randomly named DLL file (rad{randomhexcharacters}.tmp.dll when dropped by Neutrino) |
| Encryption Algorithms | AES-256 (touted to be RSA 4096 in the ransom notes) | RSA and RC4 combination |
| Number of File Types Encrypted | 901 | 933 (4.001 and 5.001) |
| Appended Extension Name | None | Replaces original file name to random hex characters: {32 hexadecimal characters}.{5 hexadecimal characters} e.g. 0412C29576C708CF0155E8DE242169B1.6B3FE |
| Scanned Drives for Encryption | D to Z, %USERPROFILE%, as well as removable and mapped network drives | B to Z as well as removable and network drives |
| Ransom Note Filename | README.TXT, README.HTML, README.BMP | !README.HTML !README.BMP |
| Autostart and Persistence Mechanisms | None | %User Startup%{unique ID}.lnk, where {unique ID} contains 12 hexadecimal characters |
| Lockscreen Capability | No | Yes |
| Anti-Virtualization and VM Check Routine | CPUID-based; runs its encryption routine even in VM and sends the information to its C&C | No VM check routine |
| Ransom Amount | 1.2 to 2.4 bitcoins (or US$792 to US$1,597 as of July 15, 2016) | 1.2 to 2.4 bitcoins (or US$792 to US$1,597 as of July 15, 2016) |
| Payment Method | Bitcoins, TOR Network | Bitcoins, Tor Network |
| C&C Communication and Information Theft | Retrieves AES key and ransom notes from C&C; sends system information and result of encryption to C&C | Retrieves RSA public key, domain information of payment site and information-stealing module (fx100.dll); sends system information and result of encryption to C&C |
| Network Activity | TCP via Port 443 | TCP via Port 443 |
| Shadow Copies Deletion | vssadmin | No |
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //