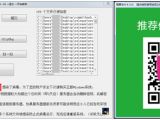
A ransomware strain dubbed "WeChat Ransom" infected more than 100,000 Chinese computers and encrypted their files asking for 110 yuan ($16) WeChat Pay ransoms to unlock their data.
The malware also steals QQ, Taobao, JD, Baidu Cloud, Alipay, Tmall, and Jingdong credentials using the Chinese Douban social network to exfiltrate them, as reported by Chinanews.
Moreover, according to Huorong's security researchers who discovered the ransomware on December 1, roughly 20,000 Alipay and Taobao username/password pairs were found on one of the servers the actors behind WeChat Ransom used to stockpile the pilfered data.
As detailed by multiple sources, WeChat Ransom's authors distribute it to their targets with the help of tens of compromised applications, with a tool designed as a management solution for multiple QQ accounts being the main propagation channel.
The massive surge in the number of infected devices between December 1 and the 100K locked computers counted by researchers on December 5 is explained by the lack of an anti-malware solution on the compromised machines.
There is also a light side to this story given that the security researchers that looked into the inner workings of the ransomware found out that it uses a very easy to decrypt algorithm allowing for multiple decryption tools surfacing since the WeChat Ransom campaign started.
Attackers mocked on social networks for asking WeChat Pay ransoms
Furthermore, a large number of victims who had their Alipay accounts stolen went on to various Chinese social networks asking the WeChat Ransom authors also to pay their credit card bills and to ask for Bitcoin during their next campaign if they want to be taken seriously.
Huorong's research team was also able to find enough traces (i.e., phone number, QQ account, email address) leading to one of the possible authors behind the ransomware attack, eventually being able to pinpoint a name used to register one of the web domain's used in the campaign.
Although at first glance the WeChat Ransom malware campaign is the work of beginners, the distribution method used to infect more than 100,000 computers shows that they have the basics covered.
If the police will not apprehend the malware's authors using the leads provided by Huorong, a future campaign might be a lot more dangerous and a lot more costly if another encryption algorithm will be used that won't allow for such quick and simple decryption.

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //