The wireless connectivity capabilities of Windows Vista have been automated to the point where the operating system will connect to a wireless network before the user completes the login process. This, of course, if Vista is configured to accomplish such a task. And in fact, these configuration settings apply mainly to internal wireless networks via Group Policy.
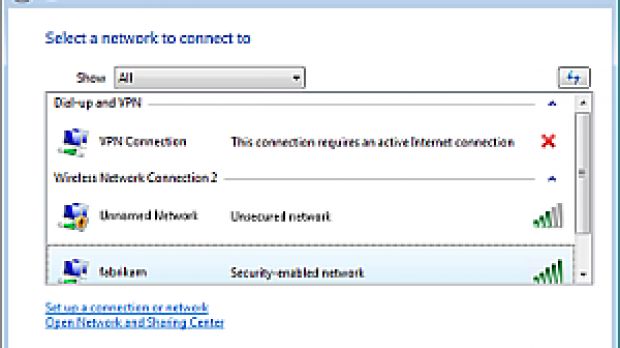
Whenever the wireless connections are not preconfigured, Vista users can click Start menu and Connect To, or right-click the networking icon in the System Tray and select Connect To, in order to access the Connect To a network wizard. The operating system will detect all available VPN, dial-up, and wireless connections and the wizard will display them accordingly.
Via the wizard, Vista users can simply select the one of the networks, or the network available and hit Connect. Windows Vista will do the rest until the connection will be complete. The user will be prompted to enter the Network Name only in the eventuality that the network does not broadcast and SSID.
User intervention will also be required if the connection wizard cannot achieve Internet access. In this context, the user will have to finish connecting to the Internet via the Web browser.
Microsoft has also prepared Vista for the worst case scenario: connectivity issues. In such a case, the operating system provides the user with two alternatives: Diagnose the problem or Connect to a different network. Selecting the first will bring up the Windows Network Diagnostics panel that does not perform the diagnosis automatically, but instead guides the user in identifying the issue.
Here is a list of the most common wireless networking problems. The Windows Network Diagnostics wizard will deliver a solution for:
- Receiving a weak wireless signal. - Having a disabled wireless radio. - Successfully connecting to the wireless networking but not receiving an IP address assignment. - Typing the incorrect security key. - Using invalid digital certificates for EAP-TLS authentication. - Experiencing hardware or driver incompatibilities. - Having authentication failures because of infrastructure failure, such as an offline authentication server.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //