In case you haven't noticed, what with the “50 Shades of Grey” hysteria taking over the world and turning it topsy-turvy, it's been another week. We are older, we are wiser and we are one step closer to seeing all our New Year's resolutions come true.
Well, those of us who haven't yet forgotten all about the things they wanted to do differently this year, that is. As per usual, researchers worldwide have kept pretty busy these past few days. So, without further ado, here are the week's best science news and announcements.
10. Scientists figured out how Richard III died
King Richard III died on the battlefield back in 1485. He was buried in quite a rush in a not-so-royal tomb that was basically a hole in the ground, and it wasn't until 2012 that his remains were finally recovered from under a parking lot in Leicester.
In a new report, researchers detail how it was that the monarch lost his life during the 1485 battle against Henry Tudor. Long story short, it looks like King Richard III was killed by a sword, spike or halberd blow to his head.
The weapon that killed the monarch entered his body through his neck, moved upwards and sliced his brain on its way, and only stopped when it hit his skull. Hence, Richard III's remains show signs of neck trauma and his skull has a dent on the inside, right where the weapon came to a halt.
Although evidence indicates that this injury was the one that killed the monarch, specialists who have had the chance to examine his body say that, during his final battle, King Richard III sustained a total of 11 injuries, some of which were quite severe.
9. NASA detailed plans to launch a submarine into space
This might sound just a tad insane, but as it turns out, NASA is seriously considering launching a submarine into space. More precisely, it wants to use such a robotic submersible vehicle to explore seas and lakes on Saturn's moon Titan.
The thing about Titan is that, contrary to what some might assume, its seas and lakes do not comprise water but are instead made of liquid hydrocarbons. NASA brainiacs expect that deploying a submarine in this rather hostile environment will help them gain a better understanding of Titan's makeup.
Truth be told, this ambitious project is, for the time being at least, merely a brilliant idea. Thus, NASA scientists say that, should such a space submarine ever be set loose in Titan's polar sea Kraken Mare, chances are that this will only happen a few decades from now, probably around the year 2040.
8. Red wine could help promote weight loss
There is nothing quite as appealing as one or two glasses of red wine to accompany a hearty steak dinner, many people agree. Interestingly enough, it looks like flavor is not the only reason guys and gals should add red wine to their menu.
Thus, researchers say that, having carried out a series of experiments in laboratory conditions, they found evidence that a compound in red wine has the potential to promote weight loss and even help fight some of the health conditions associated with obesity.
The compound in question goes by the name of ellagic acid. Apparently, it can not only limit the growth of fat cells in the body but also limit the formation of new fat cells and make it easier for the liver to metabolize the fatty acids coming its way.
Even better, it looks like this compound that might promote weight loss is naturally occurring not just in red wine but also in red grape juice. What this means is that there is no reason teetotalers should not benefit from its fat-fighting abilities as well.
7. An elephant made love to a manatee, sort of
OK, this didn't actually happen. What happened was that scientists exploring mountain forests in France came across a previously undocumented fern that, genetically speaking, is kind of, sort of like the love child of an elephant and a manatee.
The fern, a photo of which is included in the gallery below, is the result of inbreeding between oak ferns and fragile ferns. Seeing how these ferns went their separate ways about 60 million years back, scientists thought it impossible for them to hook up and have babies together.
This is because it was believed that, over the course of 60 million years of evolution, the plants must have become genetically incompatible with one another. Still, this did not happen. On the contrary, oak and fragile ferns still have the hots for each other, and their newly discovered baby proves it.
6. New form of HIV documented in patients in Cuba
A new science paper details the discovery of a previously undocumented form of HIV in patients in Cuba. The trouble with this newly discovered HIV variant is that, unlike its siblings, it is surprisingly aggressive, researchers warn.
More precisely, it appears that guys and gals infected with this form of HIV risk progressing to AIDS in just 3 years. In other words, they risk getting sick long before they even realize that they are infected with HIV and seek medical help.
It is believed that this new HIV variant is the result of recombinations of various strains of the virus that occurred in the body of patients infected with more than just one form. Apparently, HIV strains have a knack for exchanging genetic material and birthing new forms of the virus.
The reason this new form of HIV progresses to AIDS much faster than other variants of the virus is that, unlike mainstream strains, it is a tad hyperactive. Thus, researchers say that it switches between anchor points on cell membranes much faster than expected.
5. Decades-long megadroughts expected to hit the US
In a new and rather worrying report, specialists warn that, as greenhouse gas emissions continue to up and fuel climate change, the US risks being hit by so-called megadroughts that could last for 20 years, maybe even 30 or 40. Such droughts will surely have a devastating impact on the country, they add.
The researchers behind this investigation say that, under a business-as-usual scenario, the chances that the US will experience decades-long megadroughts by the end of this century revolve around 80%. These droughts will all be the result of man-made climate change.
Even more worrying, it appears that the country risks struggling with water availability even if greenhouse gas emissions are reduced in the years to come. In fact, it is said that limiting pollution will not completely eliminate the risk of megadroughts, but instead only bring it down to 20%.
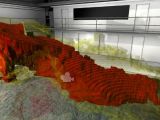
4. Huge tornado successfully recreated in 3D
Back in May 2013, a huge tornado hit the city of Moore in Oklahoma and killed a total of 24 people. With the help of some seriously high-tech equipment, scientists managed to recreate this extreme weather even in 3D and study it in unprecedented detail.
This little project was carried out inside a research facility dubbed the Cube. To recreate the May 2013 tornado in 3D, brainiacs used radar data detailing just how much water the storm dumped on the city of Moore when it hit it, as well as the speed of the particles moving through the air during this event.
Once the 3D replica of this tornado was completed, meteorologist Jim Cantore put on a virtual reality headset and got busy exploring it. He got to see not just the rain and the winds unleashed by the May 2013 storm but also how they hit the city of Moore.
Specialists say that, by creating virtual replicas of extreme weather manifestations and exploring them, they can gain a better understanding of how and why specific types of storm form. This can help deliver more accurate weather forecasts and even save lives.
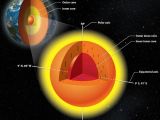
3. Earth's inner core found to host its own inner core
Brainiacs have been studying our planet's anatomy for centuries now. However, it looks like Earth still holds a whole lot of secrets that are yet to be unveiled. For instance, it would appear that researchers have plenty left to learn about what our planet looks like on the inside.
In a recent paper, scientists explain how, having taken the time to study how seismic waves move through Earth's entrails, they found evidence that there is more to our planet's anatomy than just its crust, its mantle, its outer core, and its inner core.
Thus, they say that, according to evidence at hand, Earth's inner core has an inner core of its own. This so-called inner inner core appears to comprise iron crystals that point east-west. Because of this, it behaves differently than the inner core, which is made up of crystals arranged in a north-south pattern.
2. Smoking found to make the brain shrink
Pretty much everybody knows that smoking is not exactly the healthiest of habits. On the contrary, it is a well-known fact that smoking can give people heart and respiratory trouble, even kill them. Interestingly enough, it looks like smoking also takes its toll on the brain.
Thus, specialists now argue that those who light up a tad too often for their own good risk having their brain shrink inside their skull. That's right, it appears that smoking can actively transform the brain in that it can trigger the death of neurons.
Even more worrying, the researchers behind this investigation explain that this loss of neurons chiefly occurs in the cortex, which is a brain region previously documented to be involved in cognitive processes such as memory, language and perception.
The good news is that, in the case of people who eventually give up smoking, the brain can recover from the damage it sustained during one's huffing and puffing years. True, this recovery process is not all that fast, but it's still better than continuing to lose neurons to tobacco smoke.
1. Bizarre smiley face caught on camera in outer space
This week, astronomers released a seriously creepy image showing a positively bizarre face smiling down on us from outer space. The image, included in the gallery below, was obtained with the help of the Hubble Space Telescope.
Mind you, this smiley face is not some alien looking to scare the bejesus out of us. It's actually an image of a galaxy cluster that is located at about 4.5 billion light-years from our planet and that is arranged in such a way that it appears to form a rudimentary portrait.
The galaxy cluster featured in this stunning and fairly peculiar Hubble Space Telescope image goes by the name of SDSS J1038+4849. It's nearly impossible to tell from this image alone, but it comprises trillions of stars, many of which are way bigger than our Sun.
This space image concludes this week's round-up of the best science news and announcements of the past few days. Be sure to check this page again seven days from now, as another round-up will surely be waiting for you.

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //