A new version of Reveton police ransomware has been discovered to have been upgraded with credential-stealing capability by implementing the latest version of Pony malware.
Pony is designed as a malware dropper and credential stealer that has been also added the possibility to steal digital currency wallets. It has been used in numerous campaigns to create botnets.
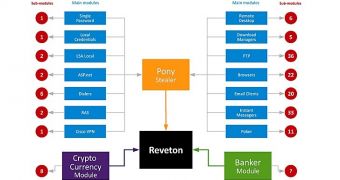
According to security researchers from Avast, the latest revision of Reveton is no longer limited to locking the computer until a ransom fee is paid, and it can also steal passwords from five crypto-currency wallets.
They also say that with the integration of the Pony component, it “affects more than 110 applications and turns your computer to a botnet client.”
Because of Pony’s capability to decrypt complex passwords stored in various forms, Reveton’s threat level has escalated significantly.
Analysis of the new Reveton determined that there are 17 main modules for stealing passwords (operating systems, FTP clients, browsers, email clients, IM clients, online poker clients, RDP/VPN clients etc.) and more than 140 sub-modules.
It also targets the most popular crypto-currency wallets and steals the access passwords. “The malware can close QT wallets and imitate the login screen after the next execute,” Avast researchers say in a blog post.
In the version they analyzed, 17 German banks are targeted and information is extracted from searches in the browser history and cookie files.
It appears that the lock screen module has also been revised by the malware author, as Reveton is now split into multiple threads, has different encryption and recreated the communication with the command and control servers.
Further firepower included in the malware refers to another password stealer, that lacks the efficiency of Pony but sports a powerful function for disabling antivirus products available on the affected system.
For cleaning the computer of a Reveton infection, Avast recommends booting into a different operating system and locating suspicious LNK files in the startup menu. These should provide the path to the binary by looking at the properties sheet, which shows the item (with CPP extension) they are assigned to.
The next stage requires deleting the LNK file as well as the binary of the malware from the link path, restarting the original operating system and observing the service that reports an error. Removing it and any “ACID” strings in the registry should be sufficient to have a Reveton-free computer at the next reboot.
All passwords should be changed in order to make sure that whatever reached the command and control server is of no use to cybercriminals.
One of the best ways to protect against ransomware with encryption capabilities is to make regular backups and store them in a location that is not connected to the computer (online or offline storage).
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //