A understudied, barely-there patch of stormy weather that developed off the western coasts of Central America appears to be responsible for the onset of the massive heat wave that affected the central regions of North America, and especially the United States.
All around the region, people have been blasted by unforgiving temperatures, which brought a host of adverse climate manifestations with them. Since it developed, experts have been trying to figure out the cause, so as to be able to discover other instances like it in advance.
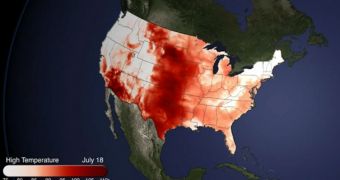
The heat wave lasted for a full week, and was described as a heat dome due to the atmospheric particularities that led to its development. Apparently, an area of high atmospheric pressure pushed down on warm air, forcing it to flow over East and Central America.
One of the things that many forgot when analyzing the heat wave is that it spans more than the US. Weather news maps only show the outline of the country, and many were limited in interpreting the storm by this fact.
However, it is sufficiently clear that the heat dome was caused by something, and the new research demonstrates that that something was located outside the United States. “Subsiding air over the United States is associated with the heat wave,” expert Kevin Trenberth explains.
“Where is the air subsiding from? There has be upwards motion somewhere,” adds the scientist, who is the head of the National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate Analysis Division.
Datasets collected by the National Weather Service’s (NWS) Climate Prediction Center show that the warm air was most likely pushed upwards by an area of heavy precipitation, which developed off the coast of Guatemala.
A pattern of heavy rains was found here between July 14-19, experts say. The discovery was made only after CPC experts began to analyze global rainfall activity maps. The central-American storm system had not been identified as a possible culprit before.
“If there’s upwards motion there, there must be downwards motion somewhere else. The odds are, that’s related to what’s going on over North America,” Trenberth explains, quoted by Wired.
The heat wave was “largely associated with weather,” the expert says. He adds that the event should not be associated with global warming. This heat wave was different from the one that affected Russia in 2010, which was indeed caused by climate change.
“They had similar temperatures, but it got stuck in place for two months. What would happen if the heat wave was stuck for two months instead of a week? We weren’t in quite the same situation,” Trenberth concludes.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //