The following tutorial will teach all Linux users how to securely wipe the free space of a hard disk drive (HDD), solid disk drive (SSD) or USB flash drive, making it impossible for anyone to recover deleted files.
In case you didn’t know, when you delete a file from your system, even from Trash, it will disappear and can’t be found anywhere on the filesystem. However, that file is not actually gone, it resides in the free space of your disk drive and can still be recovered with data recovery applications.
For this tutorial we will provide two methods. The first one uses an application called Wipe Free Space, created by Polish developer Bogdan Drozdowski. In the second method we will use the well known BleachBit software.
While BleachBit is a graphical application, the Wipe Free Space is a command-line software. However, the developer also created an easy-to-use graphical user interface (GUI), allowing novice users to employ it in order to securely wipe the free space of their disk drives.
Editor's note: Before we proceed, it is important to know that the applications will wipe the free space in unused clusters and blocks, in partially used blocks a.k.a. “slack space," as well as the names of deleted files and any other data that can be used to undelete the respective files.
Method 1 - Wipe Free Space & Wipe Free Space GUI
The Wipe Free Space command-line application can be easily installed from the default software repositories of your Linux distribution, by using the provided binary file for RPM-based Linux distribution or by compiling the sources.
After installation, you can download the GUI front-end from here, save it on your home folder, extract it, and double click the run.sh file (or execute sh run.sh in a terminal window) to open the application.
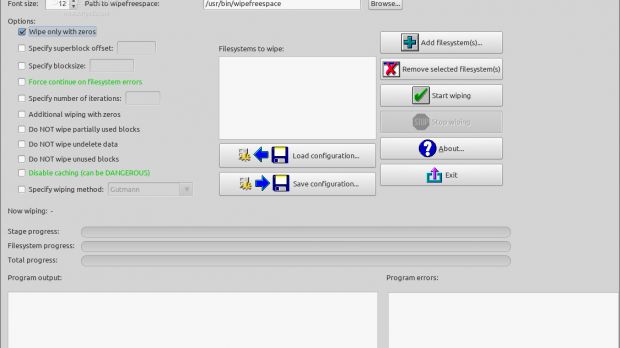
With the application opened, you will need to add the path to the wipefreespace executable, so click the "Browse" button and search it under /usr/bin/. Then add the filesystem that will be wiped.
Make sure that you check the "Wipe only with zeros" option on the left side of the window. If you need to add more options, first document yourself on how to use them, because they may crash your drive. Now press the "Start wiping" button to proceed.
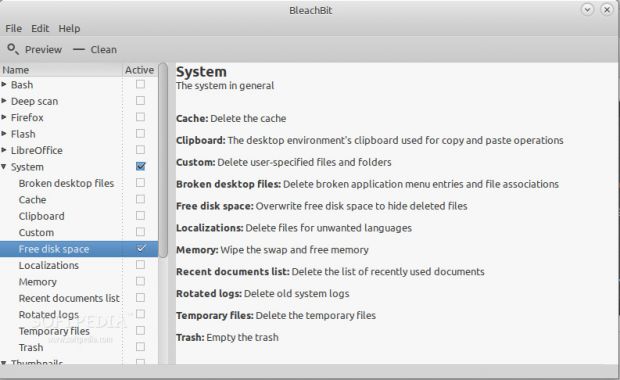
Method 2 - BleachBit
This is the easy method, recommended for novice users. You can easily install the BleachBit application from your Linux distribution's default software repositories. Open it, and make sure that you check the "Free disk space" option under the System section on the sidebar. Press the "Clean" button to proceed.
The entire wiping operation will take a long time. You can see the entire progress in the main window. Do not hesitate to drop a comment below if you encounter any issues with this tutorial.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //