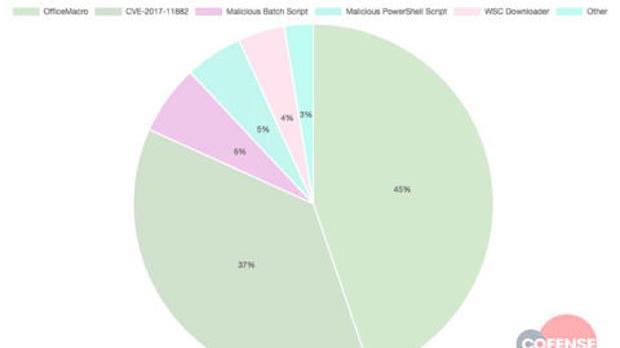
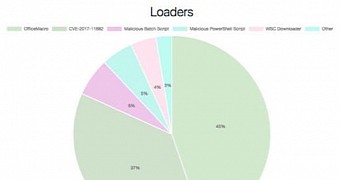
While analyzing the delivery mechanisms used by threat actors during August 2018, Cofense Intelligence found that Microsoft's Office macros account for almost half of all malware payloads delivered to targets.
As explained in their analysis, bad actors tend to use Microsoft Office macros as the first stage of infection chains and as the primary way of delivering malicious programs in about 45% of security incidents.
Office macros are one of the favorite tools attackers employ to deliver malware because on most computers running Microsoft Office the Office macro feature is enabled by default, while in organizations which have more strict security policies and the feature is disabled, end users can dismiss it with a mouse click.
The almost unnoticeable way Microsoft Office alerts users of a possible threat and the trivial method of bypassing such notices are the main reason why attackers use macros as part of their infection chains.
Office macros have been used to deliver anything from inconsequential bots to very dangerous ransomware payloads
Office macros can easily be transformed in malicious tools with the help of specially crafted Visual Basic scripts which allow bad actors to either download or run payloads from remote servers on the target machine.
Although using macros as e-mail attachments to infect computers might seem like something only low-tier threat groups or actors would use, Cofense Intelligence found that they were also used to deliver complex and very dangerous such as Geodo, Chanitor, AZORult, and GandCrab.
According to Cofense Intelligence's report, Office macros have been detected distributing anything from simple bots to highly dangerous ransomware payloads that could cripple an entire enterprise network.
As mitigation measures, the anti-phishing solution provider recommended disabling macros when in an enterprise environment, either by whitelisting the sources from which employees can receive Office documents with macros or by using anti-malware software capable of detecting and blocking malicious macro components.
According to Cofense Intelligence, #malware being delivered via #macros to be amongst the most malignant of today’s threat landscape, including: #Geodo, #Chanitor, #AZORult, and #GandCrab. Get the scoop in this week's detailed threat intel analysis: https://t.co/IcjSPraIRP pic.twitter.com/ZxUJfjo0f2 — Cofense (@Cofense) September 14, 2018
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //