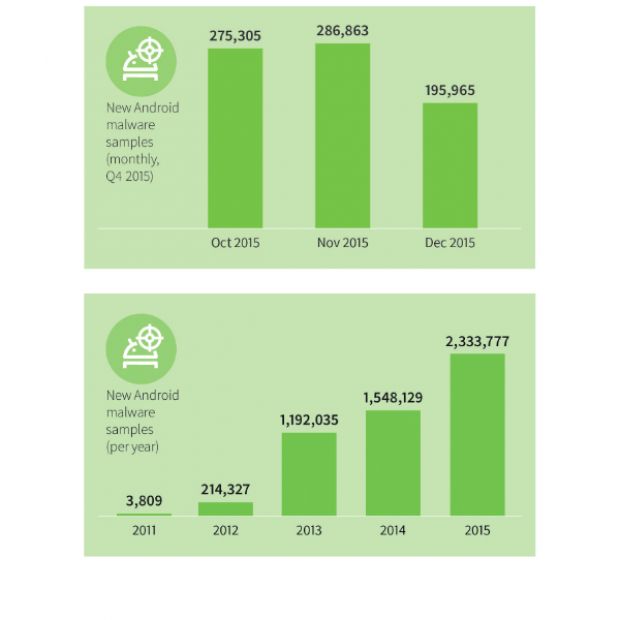
According to German cyber-security firm G DATA, during 2015, a new Android malware sample appeared every 11 seconds, for a total of 2,333,777 malware samples for the whole year, an all-time record and 50% more than 2014's total of 1,548,129 samples.
These revelations reached us via G DATA's Q4 2015 Mobile Malware Report that also reveals that during the last quarter of 2015, researchers also came across 758,133 new Android malware files, an increase of 32% from the previous quarter.
Additionally, the company also noticed that during the past year criminals put together 2.5 different malicious Android apps to spread their (new and old) malware families.
Some of the reasons behind this assault on Android devices is the fact that Android market share continues to be as high as it ever was while users are starting to use their smartphones and tablets more and more for financial and banking operations.
Since most crooks are motivated by financial gains, they tend to follow the money, and so, have expanded their malware arsenal to include more tools that target the Android ecosystem.
Malware also grew in sophistication, not just numbers
But the increase in new malware samples is not just your run-of-the-mill viruses. Just in the past month, researchers from various security companies have discovered extremely complex Android malware, mainly targeted at stealing financial information.
Some of the most dangerous ones are the Acecard, Xbot, Mazar BOT, and Asacub. families, most of which combine features from banking trojans, information stealers, and even ransomware.
G DATA researchers also say that a reason for the increase in mobile malware is also the Internet of Things (IoT). Many of these Internet-connected devices hold quite sensitive information and are sometimes managed through mobile apps.
Targeting flaws in these mobile apps sometimes helps hackers get to the IoT device, at times using the mobile app as a persistent infection point when the device's firmware can't be modified with a bootkit component.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //