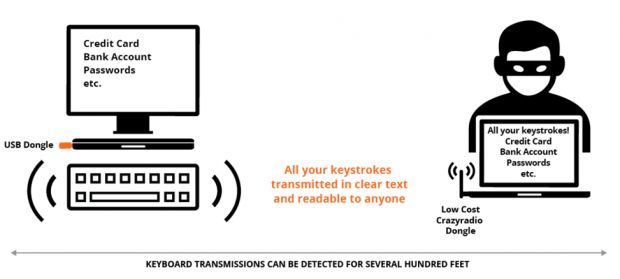
Attackers can intercept keystrokes from wireless keyboards as they are transmitted to nearby computers, can log sensitive data, or even inject malicious commands in the stream of keystroke data.
According to Bastille, the security vendor that discovered this issue, this vulnerability, which they nicknamed KeySniffer, affects wireless keyboards from vendors such as Anker, EagleTec, General Electric, Hewlett-Packard, Insignia, Kensington, Radio Shack, and Toshiba.
The company informed all affected vendors, but none issued an official response prior to the publication of their findings. Bastille also says they tested only a few products from the above-mentioned vendors, and other product series of wireless keyboards may also be affected.
KeySniffer attack is MouseJack on steroids
Bastille is the same company that at the start of the year discovered the MouseJack vulnerability that allowed an attacker to pair rogue mouse/keyboard to USB dongles used by various wireless mouse and keyboard vendors.
The KeySniffer vulnerability is an escalation of MouseJack, but instead of pairing a rogue device, KeySniffer allows an attacker to snoop on the data exchanged between the wireless keyboard and the user's USB dongle.
No wireless mice are affected by KeySniffer, and attackers can also inject rogue keystrokes inside the data stream established between a vulnerable wireless keyboard and its dongle.
The problem: Wireless keyboards are exchanging data in cleartext
All data exchanged between vulnerable keyboards and the USB dongle plugged into the user's computer is handled in cleartext, allowing the attacker to detect what victim is typing. This lack of encryption also allows them to inject their own keystrokes in the data stream.
The attacker only needs a specially crafted device that they must plug into one of their USB ports, which is nothing more than a modified antenna. The entire device costs no more than $100. An attacker can execute KeySniffer attacks from several hundred feet away.
The attacks can be carried out in a crowded mall, cafe, or enterprise network. The attacker can log anything from credit card details when users make online payments, to passwords when logging into their online accounts.
If the attacker wants to inject rogue keystrokes, they can automate their attack via scripts. The only condition is to wait for the user to leave their computer for a few minutes or seconds.
Most operating systems are designed to provide keyboard-based controls in case the mouse physically fails, so having control over a user's keyboard is like having control over their entire computer.
KeySniffer flaw is unpatchable
At its core, the KeySniffer attack relies on techniques used to reverse-engineer undocumented transceivers that were presented at the Hack in the Box Security Conference in Amsterdam. Bastille says that all of the wireless keyboards vulnerable to KeySniffer operate in the 2.4GHz ISM band using GFSK modulation.
"The transceivers used in wireless keyboards vulnerable to KeySniffer are inherently insecure due to a lack of encryption, and do not support firmware updates," Bastille explains.
As such, the company recommends that "users of vulnerable keyboards should switch to Bluetooth or wired keyboards in order to protect themselves from keystroke sniffing and injection attacks."

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //