iPad and iPhone apps signed with an enterprise certificate can be used to replace legitimate software installed from App Store, if they both have the same bundle identifier, leaving the door open for compromise of both jailbroken and non-jailbroken devices.
The vulnerability was disclosed to Apple on July 26 by researchers at FireEye, who discovered it in iOS 7.1.1, 7.1.2, 8.0, 8.1 and 8.1.1 beta; as per App Store information on October 27, versions 7 and 8 of the operating system account for 95% of the iOS installations.
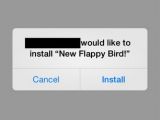
Masque Attack lures users into installing rogue app
Researchers Hui Xue, Tao Wei and Yulong Zhang from FireEye say that the vulnerability exists because certificates of apps with the same bundle identifier are not verified in iOS.
Enterprise certificates are used for signing proprietary software that can be used in corporate environment without going through Apple’s security review process.
FireEye calls this form of abuse Masque Attack because the user is tricked into installing a rogue app from a third-party store that replaces an authentic one already available on the device.
The local data of the original software is not removed, which gives an attacker access to confidential details, and if login tokens are available, to online accounts.
A Masque Attack can be used to impersonate applications with sensitive information, such as those intended for online banking or email exchange.
Only apps added from the Apple marketplace are susceptible to this kind of attacks, those that are pre-installed on the device remaining unaffected.
“Attackers could mimic the original app’s login interface to steal the victim’s login credentials. We have confirmed this through multiple email and banking apps, where the malware uses a UI identical to the original app to trick the user into entering real login credentials and upload them to a remote server,” the researchers say in a blog post.
Attack is difficult to detect, already spotted in the wild
It appears that the mobile device management (MDM) interface is unable to distinguish between two different pieces of iOS software sharing the same bundle identifier, making the attack all the more difficult to detect.
FireEye disclosed this vulnerability on Monday, after researchers at Palo Alto Networks published the discovery of WireLurker, a Trojan for the iOS platform that at times relies on the Masque Attack to compromise non-jailbroken devices when they connect to an infected computer via USB.
Versions of the malware have been found for both OS X and Windows platforms, with no major differences between them.
Keeping safe from these attacks is possible, even if no patch from Apple exists at the moment. The first rule is to install apps only from trustworthy sources and avoid third-party stores or download locations that are from unverified parties.
Secondly, the iOS shows an alert in case software from an untrusted developer is launched, which should lead to immediate uninstallation of the item.

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //