Google rolled out the January 2017 Android security updates only a few days ago, and in documentation posted on the official website, the company reveals that these fix a total of 95 vulnerabilities in the mobile operating system.
Google says that there are 22 critical vulnerabilities patched by this release, and the company confirms that most of them affect its own devices as well, including the Google Pixel and the Nexus.
The update cycle is split into two parts, both of which are shipped together to Android devices and fix remote code execution (RCE), elevation of privilege, information disclosure, and denial of service vulnerabilities either in the operating system or in its core features.
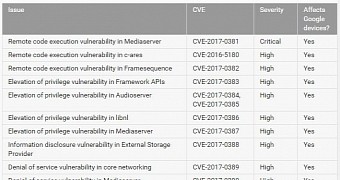
The 2017-01-01 security patch level comes with fixes for a total of 23 vulnerabilities, out of which only one is labeled as critical. It’s called “remote code execution vulnerability in Mediaserver,” and comes to resolve security bugs in a module that has often been targeted by cybercriminals with exploits in the previous months.
There are also patches for audio server, networking, external storage, contacts, and telephony modules. Aside from the critical vulnerability, there are 14 others labeled with a high severity rating, and 8 with moderate.
Qualcomm bootloader also patched
There is also the 2017-01-05 security patch level, which brings many more critical fixes, the majority of which address elevation of privilege vulnerabilities in essential parts of the Android operating system, including the kernel memory subsystem, the Qualcomm bootloader, and the NVIDIA GPU driver. There are 10 different vulnerabilities in Qualcomm components (rated as critical), but Google says that these do not affect its own devices.
One particular patch that Google users should be aware of targets an elevation of privilege vulnerability in NVIDIA GPU drivers, and which also impacts Pixel and Nexus phones. A total of 10 flaws have been discovered in the drivers, and all of them are rated as critical, as they would allow an attacker using malware to infect an unpatched device to gain rights to install additional apps.
It goes without saying that users are strongly recommended to download and install the latest patches as soon as possible. A recent study has shown that the number of Denial of Service vulnerabilities in Android is growing at an alarming rate, so it's critical for users to patch their devices fast.
After installing the updates, the information screen of your Google device should display January 05, 2017 as the security patch level.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //