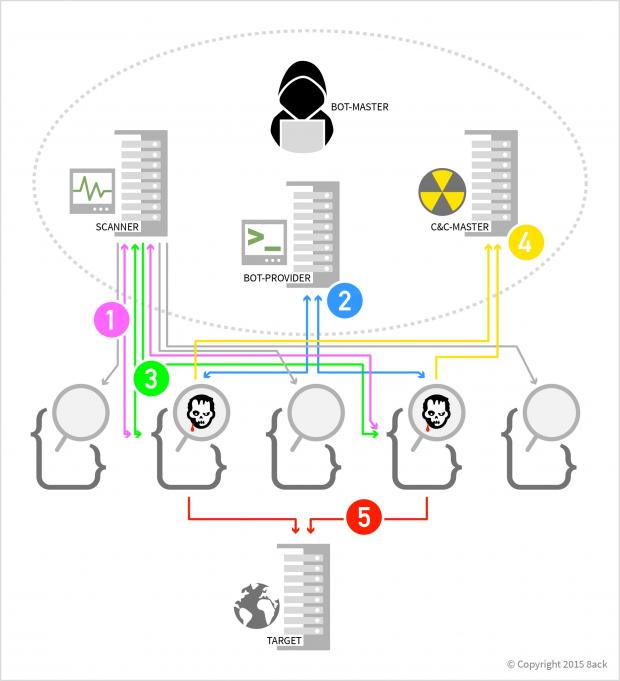
A honeypot experiment ran by 8ack, an AlientVault partner, has shown that the recent security vulnerabilities discovered in Elasticsearch servers over the summer are now actively being used by botnet operators.
The experiment ran for over three months and collected data from 30 different botnets. Internet-exposed servers used in the honeypots were running known vulnerable versions of Elasticsearch, on 32- and 64-bit Linux setups.
Elasticsearch is not a Web server, but a search server based on Apache Lucene, used in enterprise setups to provide better search results than your regular regex matches.
During the past year, vulnerabilities like CVE-2015-1427 and CVE-2015-5377 drew the attention of malicious actors to this open-source, enterprise-level technology.
Over 30 bots detected in a 3-month period
According to 8ack, 3-4 days after the honeypots were installed, they saw the first automated vulnerability scanners go over the server's setup, with full exploits soon following through.
Over 30 bots landed on the honeypots, but for various technical or configuration reasons, only 15 executed their payload.
8ack categorized the bots that executed in two categories:
► fBots: Fire & Forget - DDoS-Bots that just execute without needing to install themselves (often referred to as BillGates/BillGates.lite) ► iBots: more sophisticated bots that install themselves in /etc or /var and have the ability download other modules/bots (referred to as IptabLex/IptabLes)
While the fBots were harmless, their more dangerous counterparts were on a level of sophistication that was very similar to that of Windows-targeting malware.
"Just three requests and you are owned," says 8ack's Markus Manzke, "and if you ran [Elasticsearch] as Root the infection would be persistent and survive a reboot."
Bots were mainly used for DDoS attacks
Once iBots made their way onto infected systems, they contacted their C&C server via obfuscated domain names or hard-coded IP addresses in their code and carried out instructions they received from their controller.
Theoretically, this can be anything from DDoS attacks to downloading other malicious payloads to compromise the target's system even further.
As for fBots, researchers saw them launch full attacks on other IPs, either on their HTTP or MySQL ports. Since the fBots operate at max speed, eating up the bandwidth with their SYN packet floods, they can be easily detected if the server administrator monitors outgoing traffic.
UPDATE: The article has been updated at the request of AlienVault to reflect the fact that one of its partners, 8ack, carried out the research.

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //