One of the aspects that has evolved in Windows 7, compared with Windows Vista, involves the operating system's capabilities to glue back together disparate fragments of files that have become fragmented as a natural consequence of hard disk use. “The defragmentation engine and experience in Windows 7 has been revamped based on continuous and holistic analysis of impact on system responsiveness,” Rajeev Nagar and Matt Garson, both program managers on the Windows 7 File System feature team, revealed.
Vista brought to the table nothing short of a handicapped defragmentation experience from the perspective of users who found what Windows XP had to offer in terms of control and information sharing more appropriate. For example, Vista's defragmentation failed to provide any detailed information related to the status of an ongoing task, because Microsoft had scrapped all UI elements providing the data to end-users.
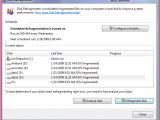
“We received feedback that you didn’t like this decision, so we listened, evaluated the various tradeoffs, and have built a new GUI for defrag! As a result, in Windows 7, you can monitor status more easily and intuitively. Further, defragmentation can be safely terminated any time during the process and on all volumes very simply (if required),” Nagar and Garson explained.
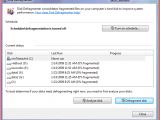
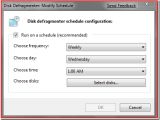
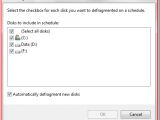
As you can see from the adjacent screenshots, the defragmentation engine now offers a level of information superior to Vista's. Yet another element that has changed is the capability of the next version of the Windows client not only to schedule a defragmentation task, but also to schedule it for multiple volumes, a functionality that is not available in Windows XP, or Windows Vista.
“Defragmentation in Windows 7 is more comprehensive – many files that could not be re-located in Windows Vista or earlier versions can now be optimally re-placed. In particular, a lot of work was done to make various NTFS metadata files movable. This ability to relocate NTFS metadata files also benefits volume shrink, since it enables the system to pack all files and file system metadata more closely and free up space 'at the end,' which can be reclaimed if required,” Nagar and Garson added.
There are two cases in which defragmentation is turned off by default in Windows 7. First off, Microsoft has disabled the feature entirely on Windows Server 2008 R2, because it can interfere and impact negatively server workloads. At the same time, the Windows 7 client will disable defragmentation by default for computers with solid-state disks. The Redmond giant informed that SSDs did not need defragmentation, and in fact the process could hurt such devices by decreasing their lifetime.
“Best practices for using defragmentation in Windows 7 are simple – you do not need to do anything! Defragmentation is scheduled to automatically run periodically and in the background with minimal impact to foreground activity. This ensures that data on your hard disk drives is efficiently placed, so the system can provide optimal responsiveness,” Nagar and Garson concluded.
Windows 7 Beta is available for download here.
Product keys to activate Windows 7 Beta are available here.

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //