Toxoplasmosis is a disease that has come to affect an increasing number of people all around the world in recent years. The infection is caused by a parasite known as Toxoplasma gondii and is spread worldwide, though it is less likely to occur in geographical areas with extremely low temperatures (like in Alaska or high altitudes) or with extremely high temperatures.
The parasite can be spread anywhere, from cat tool to food. In cats, the parasite is formed in their bowels and this is how it comes to infect their faeces. Everything that is further touched or comes into contact with cat tool becomes, in turn, infected with the parasite - humans, other animals, soil, fruits, vegetables, water etc.
The parasite may also lie in meat - all kinds of meat, especially pork, lamb and venison. When cooked properly, the parasite is annihilated by the high temperature used for frying or boiling the specific dish. But when raw or undercooked, the parasite remains in the meat.
Other sources of infection with the Toxoplasmosis gondii parasite are goat milk that is not boiled previously, through the transplant in of an organ from an already infected person or the transfusion with infected blood.
Normally, our immune system is strong enough to neutralize the parasite. But the parasite can become extremely harmful to individuals that suffer from severe immune system diseases. It is easier for the parasite now to install itself in the body and cause progressive and degenerating infection.
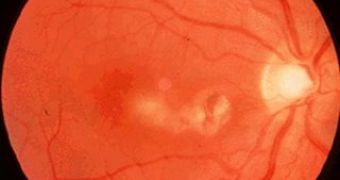
If a woman becomes infected with the toxoplasmosis parasite when carrying a baby, the infant can be infected via the placenta. The infants that are infected can develop severe symptoms of toxoplasmosis that lead to brain and eyes damage. However, there are cases when babies, even if infected as embryos in the uterus, do not develop any symptoms of the infection.
Even when contracted, the parasite grows silently into one's body and does not give any "signs" that it is inside. Therefore, most people infected with Toxoplasma gondii parasite show no symptoms of the disease. However, there is a reduced number of individuals that show signs and symptoms very similar to those of influenza or mononucleosis, like swollen lymph nodes, fever, sore throat, fatigue, body aches etc. If one does not have a weakened immune system he has nothing to worry about, as the symptoms are usually mild.
On the other hand, those with damaged immune system, like in the case of AIDS and cancer patients, are more likely to develop severe infections from the parasite. The symptoms will consist in lung disorders, extreme inflammation of the retina, headache, dizziness, confusion etc.
Besides pregnant women and individuals that suffer from AIDS and cancer, other people highly exposed to damage from the toxoplasmosis parasite are the ones that undergo chemotherapy or who take steroids or other immunosuppressant drugs.
In many cases the parasite cannot be tracked down into our bodies and that is why it cannot be treated properly until toxoplasmosis becomes acute. Then the physician can prescribe a range of medicines that will ease, reduce and possibly reverse the symptoms. However, prevention should be paid more attention than treatment, because the "silent microscopical enemy" can lead in some cases to complications and severe health disorders.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //