A self-proclaimed grey-hat hacker has located a critical SQL injection vulnerability in a website belonging to security giant Symantec. The flaw can be exploited to extract a wealth of information from the database including customer and admin login credentials, product serial numbers, and possibly credit card details.
The flaw was found by a Romanian hacker calling himself Unu, who claims that an insecure parameter located in a script on the pcd.symantec.com website allows a blind SQL injection (SQLi) attack to be performed. In such an attack, the hacker obtains read and write permissions to the underlying database.
During a regular SQL injection, the result of a rogue SQL query is displayed inside the browser. However, in the case of blind SQL injection, the queries execute, but the website continues to display content normally, making it much more difficult to extract information.
The content of the pcd.symantec.com website is in Japanese, but from what we could determine, it serves a product called Norton PC Doctor. Because accessing most of the website's sections requires authentication the hacker had to use a few specialized tools in order to exploit the vulnerability.
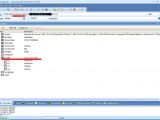
The Web server appears to be running Microsoft IIS 6.0 with ASP support on Windows Server 2000 and Microsoft SQL Server 2000 as database back-end. From Unu's screenshots there are many potentially interesting databases, but the one he chose to look at is called "symantecstore."
One of the tables in this database is named "PaymentInformationInfo" and contains columns such as BillingAddress, CardExpirationMonth, CardExpirationYear, CardNumber, CardType, CcIssueCode, CustomerEmail, CustomerFirstName, CustomerLastName or SecurityIndicator.
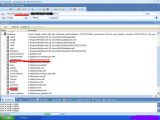
Unu claims that his interest is only to point out security issues and not misuse any data. According to him, he did not attempt to extract any information from this table. Instead, he focused his attention on another one called TB_MEMBER which contains 70,356 records.
For demonstration purposes, he extracted 6 of these entries at random, revealing customer names and login credentials with the passwords stored in plain text; a major security oversight. The hacker also claims that passwords for accounts in a different table called TB_EMPLOYEE are also stored in a similar insecure way.
A third table Unu chose to investigate is called TB_ORDER and contains columns such as ProductName, ProductNumber, SaleAmount and SerialNumber. There are 122,152 entries in the SerialNumber column.
This is not the first time when Unu scrutinizes the security of websites belonging to antivirus vendors. His previous targets includes Kaspersky and Bitdefender. Some months back, he even disclosed a vulnerability affecting a different Symantec website. The AV company eventually played down its impact.
At the end of his report, Unu mentions his previous attack against Kaspersky's US online store website. "There was fair play, they quickly secured vulnerable parameter, and even if at first they were very angry at me, finally understood that I did not extract, I saved nothing, I did not abused in any way by those data found. My goal was, what is still, to warn. To call attention [sic.]," the hacker writes.
Note: We have alerted Symantec about the potential security breach. We will update this article when/if more information becomes available. Update: In an e-mail to Softpedia, Symantec has confirmed the existence of a vulnerabiliy in the pcd.symantec.com. Here is the full statement we received:
"A SQL injection vulnerability has been identified at pcd.symantec.com. The Web site facilitates customer support for users of Symantec's Norton-branded products in Japan and South Korea only. This incident does not affect Symantec customers anywhere else in the world.
"This incident impacts customer support in Japan and South Korea but does not affect the safety and usage of Symantec's Norton-branded consumer products. Symantec is currently in the process of updating the Web site with appropriate security measures and will bring it back online as soon as possible. Symantec is still investigating the incident has no further details to share at this time."

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //