Talking about being in the right place at the right time, this is exactly what allowed ESA's Cluster spacecraft to make a startling discovery. The Cluster mission is an European Space Agency (ESA) unmanned space mission mission to study the Earth's magnetosphere using four identical spacecraft flying in a tetrahedral formation.
What the spacecraft discovered amazed astronomers: a shock wave that kept breaking and reforming , a model predicted only in theory but never actually seen in space.
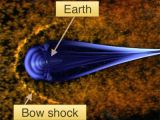
The shock wave is a natural phenomenon found above the Earth's surface, on the side facing the Sun, at 96,100 kilometers (59,700 miles), at around a quarter of the distance to the Moon and it's produced by the flow of electrically charged particles from the Sun entering Earth's magnetic field .
As the particles collide with the magnetic field, they're rapidly slowed, causing a barrier of electrified gas, called the bow shock, to build up, much like water is pushed to the sides by the nose of a boat.
The reforming of this wave was theorized 20 years ago, but it's the first time it was recorded. The recording was made as the four spacecraft, traveling at 600 kilometers from each other, approached the bow shock.
Instead of reading a similar signature form all four ships, as expected, they showed large fluctuations in the magnetic and electric field surrounding each spacecraft, along with marked variations of the protons in the solar wind that were reflected by the shock back to the Sun.
"The features derived from three different scientific experiments on the Cluster satellites provide the first convincing evidence in favor of the shock reformation model," says Vasili Lobzin of the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Orl?ans, France, who headed this study.
As bow shocks around faraway celestial bodies are linked to some of the most energetic events in the Universe, the reports of their reforming has significant implications for future investigations.

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //