IT security firm McAfee has published the “McAfee Labs Threats Report: Fourth Quarter 2013.” The report focuses on the connection between the underground market and the recent increase in point-of-sale (POS) attacks.
Experts highlight the fact that many of the attacks involving POS malware have relied on relatively unsophisticated technologies. Most cybercriminals simply purchased “off the shelf” malware from underground markets and customized them to meet their specific needs.
Researchers have uncovered a total of 40 million payment card records being sold on cybercrime websites. Most of the information has been stolen in 1-4 million batches.
“The fourth quarter of 2013 will be remembered as the period when cybercrime became ‘real’ for more people than ever before,” noted Vincent Weafer, senior vice president for McAfee Labs.
“These cyber thefts occurred at a time when most people were focused on their holiday shopping and when the industry wanted people to feel secure and confident in their purchases. The impact of these attacks will be felt both at the kitchen table as well as the boardroom table,” Weafer added.
“For security practitioners, the ‘off the shelf’ genesis of some of these crime campaigns, the scale of operations, and the ease of digitally monetizing stolen customer data all represent a coming of age for both Cybercrime-as-a-Service and the ‘dark web’ overall.”
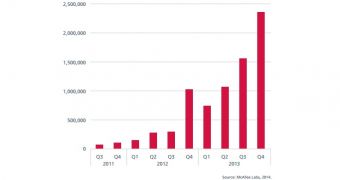
In addition to POS attacks, the report also highlights the increase in signed malware. McAfee says its database contains over 8 million samples, 2.3 million of which were discovered in Q4 of 2013.
The samples include malware signed with stolen, purchased or abused digital certificates. However, experts believe the 52% increase is due to rogue Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
These services enable cybercriminals to distribute malware by wrapping it in a signed installer.
“Although the expansion of the CA and CDN industries has dramatically lowered the cost of developing and issuing software for developers, the standards for qualifying the identity of the publisher have also decreased dramatically,” Weafer said.
“We will need to learn to place more trust in the reputation of the vendor that signed the file, and less trust in the simple presence of a certificate.”
In addition to POS attacks and digitally signed malware, the report also reveals that the number of new mobile malware samples has increased by 197% compared to the end of 2012.
As far as ransomware is concerned, their number has doubled since the fourth quarter of 2012.
The complete McAfee Threats Report for Q4 2014 is available on the company’s website.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //