A team of researchers from Biotech Research and Innovation Center (BRIC), at the University of Copenhagen, have found for the first time a protein within the body that can be very effective in preventing chronic tissue inflammation.
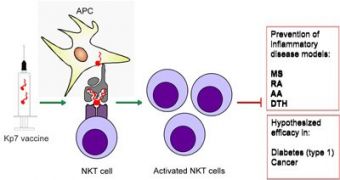
It can prevent and treat several inflammatory disease models for multiple sclerosis (MS), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), skin hypersensitivity and allergic asthma (AA), if administered as a therapeutic vaccine.
This new vaccine simply stimulates a special kind of cells in the immune system, called NKT cells – a type of T cells that have a very string regulatory effect in disease, going from autoimmunity in response to pathogens, to cancer.
NKT cells have been discovered for nearly twenty years now, and scientists believed that they were activated by lipid antigens presented by CD1 molecules.
Principal Investigator Shohreh Issazadeh-Navikas, the Danish lead researcher of the study, along with researchers from Sweden and Germany, have published an article which presents their work as the highest point of a ten-year research for ways to fight inflammation and inflammatory diseases.
Their accomplishments are very important, since they are the first to prove the ability of a self peptide to activate NKT cells and put an end to many tissue-specific inflammatory conditions including experimental autoimmune diseases.
This research offers new insight into the way that the body fights inflammation while being healthy or when suffering from disease.
The researchers also found out what was necessary for the activation of the cells, and the signaling pathway through which they exercise their function.
“The implications of the findings are large as they shed light on an important way that the body combats inflammation and autoimmunity,” said Professor Issazadeh-Navikas.
“Moreover, they establish a therapeutic approach for using the newly discovered protein as a treatment for multiple conditions.”
She highlighted, the “data offer a novel perspective on the physiological role of these cells in maintenance of tissue homeostasis and reduction of inflammation.”
These findings are a huge step forward into the fields of autoimmunity, antigen presentation, and NKT cells, because they give precious information about the biology of these cells and their roles in disease, pointing the way to effective new therapies.
The article the researchers published is entitled 'Endogenous collagen peptide activation of CD1d-restricted NKT cells ameliorates multiple tissue-specific inflammation in mice', and it appears in the prestigious Journal of Clinical Investigation.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //