A third variant of the NotCompatible Trojan that recruits Androids into a botnet has been uncovered and analyzed by security researchers, who found its communication infrastructure to be the most complex for mobile devices.
According to the research, the technological innovation has matured to the point that it rivals that seen for desktop computers.
Social engineering seems to be the method used by cybercriminals to distribute and trick users into installing the malware. In an email message, it has been observed that the potential victim was requested to install a security update in order to have access to an attached file.
Lookout has been monitoring the Trrojan since 2012, when it was used as a proxy on infected devices for deploying spam campaigns.
Complex infrastructure makes it difficult to detect
The latest variant has behind it peer-to-peer communication, encryption, and a server architecture that makes it “elusive and enduring.”
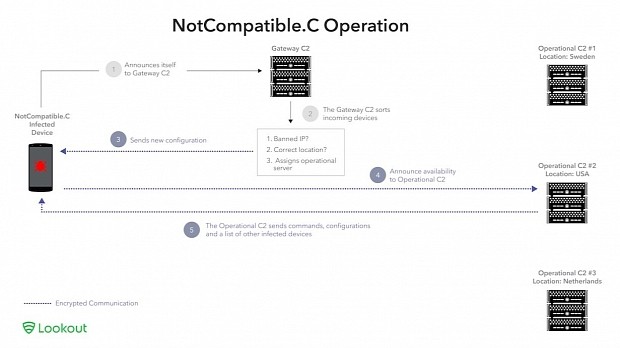
“NotCompatible.C, however, employs a two-tiered server architecture. The gateway command and control (C2) server uses a load balancing approach, in which infected devices from different IP address regions are filtered and segmented geographically, and only authenticated clients are allowed to connect,” says Tim Strazzere from Lookout in a blog post.
This is more than just a model of efficiency in terms of client usage, but it is also a way to avoid discovery, the researchers suspecting that behavioral analysis systems are hindered in detecting the traffic by the gateway server, which delivers information about active command and control servers.
According to Lookout, there were more than ten C2 servers up and running, located in different countries, such as Sweden, Poland, Netherlands, the UK, and the US.
The data from the gateway is shared with other infected devices, creating redundancy and thus ensuring a defense against takedown. Intercommunication of the compromised Androids makes it easy to find a new command and control server to connect to in case the original one(s) is no longer controlled by the cybercriminals.
Another innovation rarely seen in the case of mobile malware is that communication is encrypted in such a way that the traffic resembles binary streams, “unremarkable and indistinguishable from legitimate encrypted traffic such as SSL, SSH or, VPN traffic.”
Compromising corporate networks not excluded
From the analysis of the botnet activity, the researchers have come to the conclusion that NotCompatible is up for renting for carrying out different malicious campaigns. Some of the uses detected include spam delivery, bulk ticket purchasing, brute-force attacks against WordPress log-in pages, and controlling other malware (c99shell – a PHP shell script that provides access to the victim’s machine).
Lookout has not seen any attacks aiming at the protected networks of companies, but given the fact that the operators of NotCompatible seem to rent the botnet, using it to assess a corporate environment is not excluded.
A scenario described by the researchers would involve an infected device being used to scan the network for vulnerable machines. Once these are found, exploits can be delivered to compromise them in order to exfiltrate useful information.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //