Heartbeat vibrations could one day power up a new generation of pacemakers, say scientists at the University of Michigan, in the US. If such a technique could be applied to devices controlling the heart beat, then the need to perform battery replacement surgery would disappear.
At this time, people who carry pacemakers need to undergo regular surgery, where doctors change the batteries powering up their medical implants. This is very uncomfortable, so scientists have been looking for ways to eliminate this procedure from their work flow for a long time.
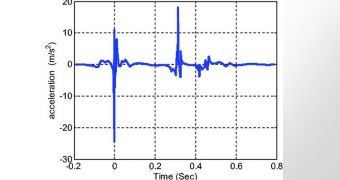
Now, U-M engineering researchers propose a new solution to this problem. They say that each heartbeat reverberates through the chest, producing small vibrations. By using a new device the team developed, it may be possible to convert these vibrations into electricity.
This energy could then be used to power up pacemakers or an implanted defibrillator. Both these tools are used to force the heart into keeping a healthy rhythm in cardiac patients. In devices implanted today, small batteries provide the needed current.
Each patient with such an implant needs to undergo surgery once every 5 to 10 years, in order to have the battery replaced. The waiting period between surgeries is determined by the volume of work the implant needs to carry out.
“The idea is to use ambient vibrations that are typically wasted and convert them to electrical energy. If you put your hand on top of your heart, you can feel these vibrations all over your torso,” U-M Department of Aerospace Engineering research fellow Amin Karami explains.
Funds for this investigation were secured from the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the Virginia Tech Institute for Critical Technology and Applied Science.
The U-M group has not yet built a working prototype. However, it did manage to develop a series of schematics and blueprints for how the vibration-powered device should look like. The most important component is a thin slice of a piezoelectric material.
Piezoelectrics are special ceramics and crystals that produce a small electrical current when a mechanical force is exerted onto them. Heart vibrations can easily distort the shape of the thin piezoelectrics slices that the team wants to use.
Details of the device are published in a paper called “Powering pacemakers from heartbeat vibrations using linear and nonlinear energy harvesters,” which appears in the current issue of the esteemed journal Applied Physics Letters.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //