Experts now propose that our galaxy features 3 galactic arms, rather than 2 proposed until now. The discovery also implies that the overall shape of the Milky Way may be a bit different than calculated based on the old data.
The fact that Milky Way is a spiral galaxy has been proposed – and widely accepted – since 1852. But researchers thus far failed to come to an agreement as to the total number of spiral arms the object has, and also on the general shape of the entire galaxy.
For example, some 20 years ago, researchers proposed that the galaxy had a central bar, and at least six arms. But verifying these information is very difficult due to the fact that stars overlap in telescope images of the galactic core.
As such, it becomes very difficult to assess which stars are close and which are far, and this would be essential to figuring out the shape of the galaxy. But more recent investigations are beginning to shed a much cleared image of the Milky Way.
For instance, the astronomical community agrees that there are only two spiral arms – Perseus and Scutum Centaurus – while the other structures are simply large gas filaments. The latest study in the field supports this idea, but also brings something extra to the table.
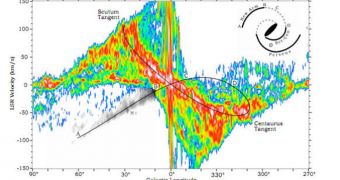
Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA) astronomers Thomas Dame and Patrick Thaddeus add that the consensus that the Milky Way has only two arms, but propose that another arm-like structure exists on the other side of the galaxy.
The structure may be located opposite to the solar system's location, but it revolves around the galactic core a lot farther than the Sun does. The new arm is hypothesized to be 19 kiloparsecs long, and to span about 50 degrees on the sky.
But this formation is most likely an extension of the Scutum-Centaurus Arm, rather than an entirely new galactic arm all on its own. If this proposal holds true, than the the Centaurus arm may in fact be just as large as the Perseus arm.
This would make the Milky Way a barred, twin spiral galaxy, that looks just like the Great Barred Spiral. The latter is located around 56 million light-years away from us, Technology Review reports.
The reason why experts could not see the extension is because it's warped, bent slightly out of shape, and a little off from the galactic plane. This may give the entire galaxy a warped appearance, as seen from the outside.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //