Jellyfish inhabit most warm and temperate seas. Over 900 species are known (the Mediterranean Sea alone harbors 180 species). In tropical regions, some jellyfish may inhabit even freshwaters. Usually they are solitary, but sometimes gather in huge numbers, forming "jellyfish soups".
In Florida, during the estival season, from March to September, one in four swimmers gets out of the water with burnings caused by jellyfish. Worldwide, 130 million tourists experience the jellyfish attack.
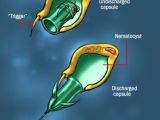
Regardless of their species, these carnivorous creatures are endowed with about 750,000 stinging cells located on their tentacles. Each cell, called nematocyst, contains a venom capsule in which a harpoon is enclosed. At the surface of each nematocyst, a small cilium, once touched by a fish or a swimmer, transmits a signal which triggers the mechanism of the nematocyst: the capsule breaks and the harpoon is launched, piercing the skin of the victim with the speed of a bullet.
The power and efficiency of this mechanism, unique amongst animals, is the high number of acting cells. A sole square millimeter of skin is attacked by 2,000 such venomous harpoons. Small preys are instantly paralyzed by the venom, which blocks their neurons, causing the explosion of the blood cells.
After the attack, the jellyfish only has to retreat its "nets" (the tentacles can be 10 m (33 ft) long at a width of 1 mm) and to swallow its victim. The used nematocysts are replaced by new ones.
Still, there are creatures immune to jellyfish venom, like the basking shark (Cetorhinus maximus), the sunfish (Mola) and even sea turtles, which can feed on box jellyfish (Chironex) whose venom can kill a man in 5 minutes! Clown fish (Amphiprion) find shelter amongst the tentacles of the sea anemones, relatives of the jellyfish, which possess equally dangerous nematocysts.
Scientists were intrigued by this ability of the clownfish. When the mucus of this fish was removed, the sea anemone harpooned and ate its companion fish. The mucus acts on the cilium, blocking its signaling. The researchers made a synthetic product mimicking the mucus of the clownfish. The product did not work only against the stinging of 15 jellyfish species (but it was not tested on Chironex). As nematocysts work on the same principle in all jellyfish species, this may work on all species. The difference amongst the jellyfish species is the composition of the venom, resulting in different powers.

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //