Windows Vista features an overhauled networking infrastructure, a completely revamped network protocol stack and IPv6 as the default protocol moving ahead from IPv4, but the operating system also includes old trusted networking tools from previous Windows platforms. IPCONFIG.EXE or simply Ipconfig and just "ipconfig" in a command prompt window is a command line tool designed to deliver TCP/IP network configuration diagnostic capabilities.
Ipconfig has survived into Windows Vista and in order to access the utility all you have to do is type "cmd" in the Search Box under the Vista Start Menu and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter in order to launch the command prompt administrative privileges. If you enter the "ipconfig" command, the utility will display all the Windows Vista IP configuration information. By default, Ipconfig will only publish the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway according to all adapters.
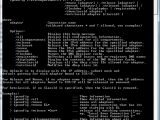
But there is more to this command line tool than meets the eye. The fact of the matter is that Ipconfig will not only display TCP/IP network configuration values but will also work in conjunction with Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) commands. However, just as it is the case with other command-line tools, Ipconfig is not intuitive, not at all. In order to access all the parameters that can be used with Ipconfig in Windows Vista use the following command "ipconfig /?".
As you are able to see from the adjacent image, there are quite a few options for Ipconfig. Followed by "/?", "/all", "/allcompartments", "/release", "/release6", "renew", "renew6", "flushdns", "registerdns", "displaydns", "showclassid" and "setclassid", the Ipconfig command-line tool will display (in the order of the parameters) the help, the full configuration, all compartments, release the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses and even renew them either for a specific adapter or for all adapters bound to TCP/IP, purge the DNS resolver cache, refresh DHCP leases and reregister DNS names, reveal the contents of the DNS resolver cache and display and modify the DHCP class IDs for the adapter.
You will be able to access additional information on Ipconfig syntax and parameters via this link for Windows XP; note that the functionality has remained virtually unchanged in Vista. However, I also want to take a minute and explain the information that Vista will display after you run the basic "ipconfig".
The Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection will show IPv6 and IPv4 addresses but also Subnet Mask and Default Gateway. Tunnel adapter Local Area Connection* 6 is related to ISATAP, but what's even more important, Tunnel adapter Local Area Connection* 7 is associated with the Teredo protocol designed to help with the transition from IPv4 to IPv6.

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //