Incapsula has been looking for a while into the activities of Semalt, a botnet that’s been quickly spreading over the Internet.
The security company says that the SEO startup has an “unscrupulous” behavior, which has caused concern to many website owners due to what’s been largely referred to as a spam campaign. Semalt seems to be ignoring “robots.txt” directives and overbearing servers with suspicious-looking requests.
Incapsula says that a few months ago they noticed the first indications of a large scale referrer spam campaign which seems to originate from Semalt. “Its bots were employing referrer spam techniques on an impressive scale, and it was aggressive enough to draw our – and our clients’ – attention,” the company states.
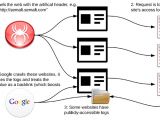
Referrer spam is done with the purpose of creating backlinks to a certain URL by abusing access logs that are available publicly. After vulnerable websites have been located, the exploit begins. The bots access hundreds of thousands of websites in bulk, sending out requests which contain the website URL that the perpetrators are trying to boost.
As people started to notice the tactics Semalt was employing and how the “robot.txt” directives were going ignored, they’ve also taken to Twitter to call them out. This happened especially after the company started sending messages to people telling them that they can exclude their sites from the database by filling in a form.
Since no one actually subscribed for this, it’s obvious that it’s spam. Furthermore, submitting the removal form doesn’t take the sites off any lists, but actually causes more spam traffic.
“Semalt is not your typical script bot. Incapsula’s analysis shows that the company uses a QtWebKit browser engine to avoid common detection methods. Coincidentally, the Semalt bot can execute JavaScript and hold cookies, thereby enabling it to avoid common challenge-based bot filtering methods (e.g., asking a bot to parse JavaScript). Because of its ability to execute JavaScript, the bot appears in Google Analytics reports as being ‘human’ traffic,” Incapsula’s report reads.
The entire situation reached another stage as evidence was found that Semalt isn’t running a regular crawler, but rather a botnet generated by malware hidden in a utility called “Soundfrost.”
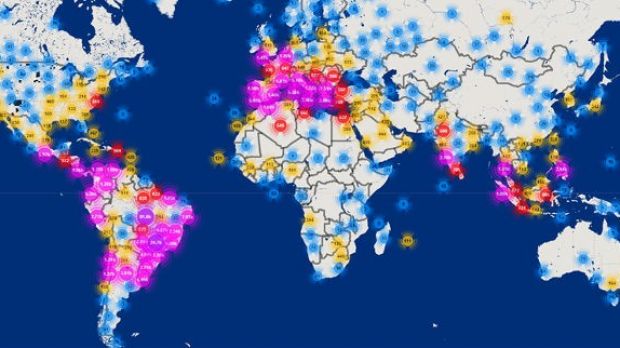
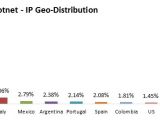
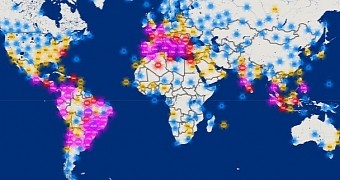
Hundreds of thousands of computers have already been infected, data shows, which means that this is a rather dangerous tool. Over the past 30 days, Semalt bots attempted to access over 32 percent of all websites using Incapsula’s services, while spamming attempts originated over 290,000 different IP addresses around the globe.
Basically, those Google Analytics data all sites can get access to may not actually be accurate due to all the activity from Semalt.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //