The recently released IBM X-Force mid-year threat report revealed a lot of interesting things about threats, security breaches, phishing and targeted network attacks.
So what do the graphs and numbers exactly reveal?
It seems as the number of SQL injection attacks has witnessed an upward trend in the first part of 2011, but according to the report, it's too early to determine the overall tendency.
While SQL injection attacks seem to rule when it comes to volume, they're closely followed by SQL_SSRP_Slammer_Worm which was seen doing its job 90 million times. The top 10 is closed by SMB_Mass_Login with just under 10 million hits.
The hourly infection attempts recorded between March 10 and March 11 show that the most attempts were made between 00:00 and the early hours of the morning GMT time.
The number of newly registered anonymous proxy websites has also grown, recording a 300% growth compared to the first semester of 2008.
Malicious websites are mainly hosted in the USA, while France, China and Romania share the same amount of malware spreading locations.
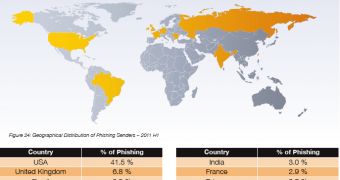
India sends a large part of all the spam emails but if we take a look at the geographical distribution of phishers we see that the USA clearly tops the chart, followed by the UK, Brazil, Bulgaria and Romania.
Software vendors seem to be more on alert when it comes to patching bugs, as in 58% of cases, the issue was remedied the same day, while only 5% came up with a solution some time later. The rest of 37%, unfortunately, still haven't come up with any results regarding their application weaknesses.
Somewhere in the paper, the hypothetical question is asked “if IBM X-Force were running the IT department and saw what happened this year,” what would they do?
Considering the increased number of breaches, companies are advised to perform regular internal and external security audits as they are the best way to ensure that the network's complete landscape is understood and the weaknesses are easily located.
Complete control over the endpoints is another important factor that must be considered. A dynamic IT environment where everything can be easily kept up to date is crucial.
Devices that store sensitive information should not be connected to unsecured components of the network and also, training activities to avoid phishing and spear phishing are recommended.
Bad passwords must be eliminated throughout the organization and the availability of a solid incident response plan could never hurt.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //