Scientists are currently working on developing a method of delivering gene-suppressing medication into the human body via creams. Nanoparticles in these substances could then pass through all layers of the skin, and enter the bloodstream.
This type of drug is very important against a large number of conditions, where gene expression may sometimes work against patients. In these instances, stopping that gene from getting expressed even further could reduce damage, and promote healing.
At this point, these drugs are delivered via injections, but experts want to have access to a much easier and convenient way of inserting them into the human body. Basically, they want to take advantage of the fact that nanoscale particles can pass through human skin.
Usually, the outer layer of the skin (the epidermis) is responsible for stopping foreign contaminants from entering the body, by acting as a kind of filter. However, there is a certain size limit below which substances can penetrate the epidermis. At the nanoscale, this is oftentimes possible.
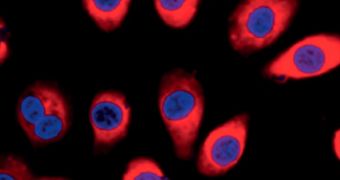
Another advantage of nanoparticles is that they do not cause any damage to skin cell membrane as they pass through. They are so small that they can even enter the cellular nucleus, where all the genetic data are stored, Technology Review reports.
Once inside, the particles delivery their payload, consisting of small interfering RNA (siRNA) molecules, which are the active ingredients in gene-suppressing therapies. Basically, these acids can control how our genetic material is expressed at any given time.
This includes the expression patterns that lead to the unfettered cell replication characteristic to cancer tumors. In other words, it is possible to use siRNA to stop the spread of cancer. Couple this with an effective, early-detection method, and you get the basis of an efficient therapy against this condition.
At this time, small interfering RNA-based therapies are among the most heavily researched areas of science. The study dealing with the effects of using nanoparticles for siRNA delivery was conducted by scientists at the University of Illinois.
The group published details of the research effort in an early July issue of the esteemed journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //