The "Open Vulnerability Assessment System" (OpenVAS) is an open source fork of the well-known Nessus vulnerability scanner. The OpenVAS project announced the first stable release yesterday.
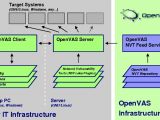
The project was born when Nessus 3 changed its licensing terms and adopted a proprietary license. Because of this, OpenVAS is an open source fork of Nessus 2.2 and it is released under the GNU GPL. Nessus is a well-known network security scanner which features a graphical user interface. The OpenVAS consists of three components: a server, a client and an NVT feed.
The OpenVAS Server is the core application that is responsible for performing the security tests on targeted systems and returning the results. The tests come in the form of plug-ins, which makes the process very flexible, allowing administrators to implement only the specific tests they require. The server package is available for several Linux distributions like OpenSuSE, Fedora, Mandrake, Gentoo, with support for Debian and Ubuntu being currently in the works, as well as FreeBSD.
The OpenVAS Client is a graphical user interface for managing and performing the tests, as well as for analyzing the results. It is forked out of NessusClient CVS HEAD 20070704 and it uses GTK+ 2.4. The fork was necessary because the NessusClient based on GTK was no longer developed, its future versions being all based on Qt. In addition to the packages for several Linux distributions and FreeBSD, the OpenVAS Client is also available for Microsoft Windows operating systems.
Finally, the third component is the OpenVAS NVT Feed. NVT stands for Network Vulnerability Tests, which are provided for the OpenVAS Server through the OpenVAS NVT Feed. NVTs come in the form of .nasl and .inc files, and are digitally signed in order to validate authenticity. Third-party developers can add their own NVTs to the Feed and the system administrators have the possibility to choose which digital keys they trust and which tests they want.
Even though for now this stable release is basically a Nessus fork, the OpenVAS project aims at improving the platform in the future, its next focus being on improving support for the NVTs, as a lot of Nessus NVTs can?t be used due to a proprietary component. It aims to make these NVTs open source, as well as to implement new ones to address current and future security issues. Working on more detailed documentation is another urgent need, according to the developers.
Users interested in details about future versions or features can check out the project?s Roadmap, or subscribe to the announcement mailing list, while interested developers are welcomed and encouraged to join the development team.

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //