Modern Honey Network (MHN) offers companies an easier way to deploy and manage honeypots as well as automate various tasks.
Built by ThreatStream cyber security company, the tool can prove to be an asset for IT security departments in companies by providing insightful information on various forms of attack used by bad actors, and it can also keep up with the latest threats.
Honeypots are monitored isolated systems acting as a decoy for intruders, which allows gathering information on the attackers. They can also confuse an intruder and thus have them spend more time on the job, allowing the security team to take the necessary precautions for protecting the real data.
They can be deployed behind the firewall and constitute an early warning system or they can function as a sink for bad IP addresses that can be incorporated into a reputation engine working at enterprise level.
Jason Trost from ThreatStream says that “deploying and managing honeypots is difficult” and that installing honeypot packages, managing the sensor, setting up data flows, and analyzing the collected information are tasks more difficult to implement than they it should be.
“Honeypots have not received wide adoption as an enterprise defense largely because the deployment and management has been a complicated process reserved for security companies and security researchers,” says the post announcing the availability of the tool.
MHN has been designed as a free alternative to the current solutions on the market that can help increase the number of production honeypots.
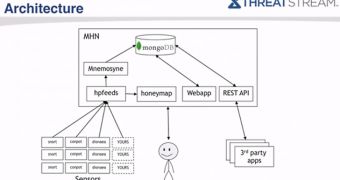
It relies on open source tools such as hpfeeds for collecting sensor data, nmemosyne for indexing the data into mongoDB, and honeymap for real-time visualization of the information.
The developer also plans to integrate support for other open source tools, such as Suricata, Kippo, Glastopf, and Shiva sensors. Trost says that support for Redhat and CentOS sensors needs to be improved, but MHN works very well with Ubuntu.
Modern Honey Network’s web application shows information about the latest attacks, offering a list of the top five attacker IPs and the ports that have been used by the intruder.
A map of the honeypot network is also available, offering real time details about attacks and an activity log.
A presentation video with the benefits of a honeypot network and how MHN can assist with deploying new decoy systems as well as monitor the activity is embedded below.
Since the project is open source, anyone can get the code and modify it in order to fit the needs of their organization.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //