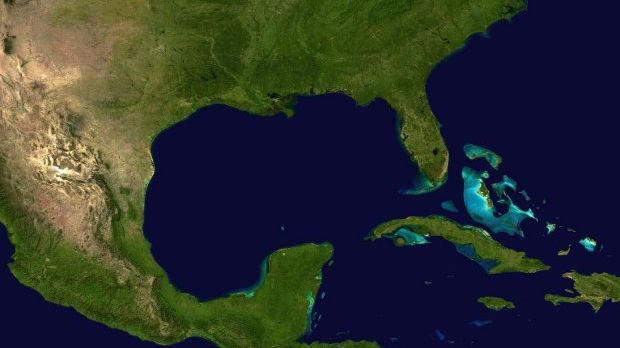
Each summer, a so-called dead zone forms in the waters of the Gulf of Mexico. In a recent report, scientists with the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration predict that this year's dead zone in the Gulf of Mexico will cover an area about the size of Connecticut.
Specifically, they estimate that it will span over 5,483 square miles (roughly 14,200 kilometers). In case anyone was wondering, last year's dead zone was documented to cover 5,052 square miles (some 13,100 square kilometers).
What's a dead zone anyway?
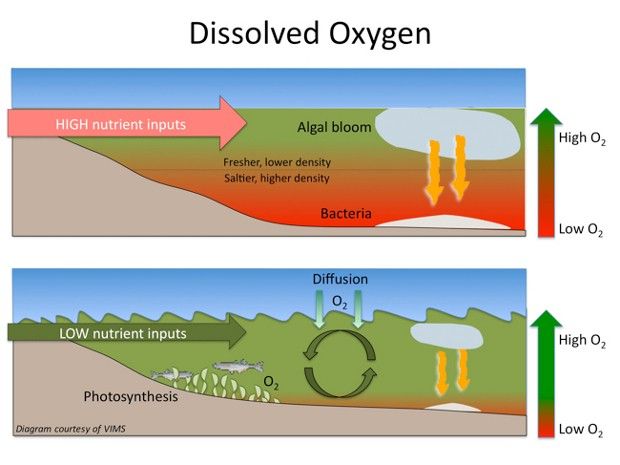
As explained in the infographic below, a dead zone, otherwise known as a hypoxic zone to the scientific community, is basically an area where oxygen levels are extremely low.
Dead zones form in the aftermath of algal blooms. In turn, such events are the result of nutrient runoffs from rivers, researchers explain.
Here's how it happens: once nutrient runoffs from all across the US reach the Gulf of Mexico, they trigger a boom in the local population of algae.
When they die and decompose, the algae are eaten by bacteria. Having plenty of food to go around, these microorganisms breed beyond control and use up massive amounts of oxygen.
To estimate how big a dead zone will grow to be, researchers need only determine the amount of runoff nutrients reaching the Gulf of Mexico to become food for algae.
This year, some 104,000 metric tons of nitrate and 19,300 metric tons of phosphorus entered this ocean basin in May alone. It might sound like a lot, but it's actually an improvement.
Thus, this year's figure is 21% and 16% lower than the 1980-2014 average for these two environmental pollutants, respectively, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration scientists say.
Dead zones are bad news
The trouble with dead zones is that they take their toll on marine ecosystems, seeing how fish and many marine plant species can't live in waters with a fairy low oxygen content.
“The low oxygen levels cannot support most marine life and habitats in near-bottom waters. The dead zone in the Gulf of Mexico affects nationally important commercial and recreational fisheries and threatens the region’s economy,” specialists say.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //