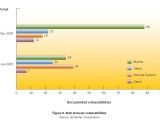
Judging strictly by the sheer volume of vulnerabilities Mozilla Firefox was the most insecure browser in 2007, according to Symantec. Firefox had a total of 122 security holes, more than any other rival browser. Symantec credited the efforts poured into securing Internet Explorer 7 for IE managing to be situated under Firefox in terms of security flaws. Internet Explorer, Firefox, Opera and Safari are together synonymous with the browser market, having divided the vast majority of the Internet audience among them. In addition to the constant race for an increased install base, the four browsers are also continually evolving toward new standards of performance, compatibility and security. In this regard, Symantec has published a report offering an insight on one critical aspect of browser security - vulnerabilities.
According to the Cupertino-based security company, there is an increasing trend for the threat environment to shift the focus of exploits and attacks toward client-side problems, with browsers growing in prominence. Obviously, no browser is a panacea to security or a silver-bullet solution, and at the same time the vulnerability count is not, in itself, a complete measure of security.
"Web browser vulnerabilities are a serious security concern due to their role in online fraud and the propagation of spyware and adware. They are particularly prone to security concerns because they come in contact with more potentially untrusted or hostile content than most other applications. This is a concern because attacks can originate from malicious Web sites or legitimate Web sites that have been compromised to serve malicious content. It is also true that browsers can play a role in client-side attacks because of their ability to invoke plug-ins and other applications when handling potentially malicious content served from the Web such as documents and media files," Symantec stated.
Firefox was impacted by no less than 88 vulnerabilities in the second half of the past year, with another 34 in the first half. Mozilla's open source browser cumulated more vulnerabilities in 2007 than any other browser, this despite the fact that Firefox is generally perceived as an apex of security. For Firefox, 19 vulnerabilities in the second half of 2007 and 12 in the first half were labeled with a severity rating of medium by Symantec, and the remaining 34 flaws in July-December 2007 and 22 in January-June 2007 were designated as representing only low-level threats.
"Safari was affected by 22 vulnerabilities in the second half of 2007. One was considered high severity, 12 were medium, and nine were low. This is a decrease from the 25 Safari vulnerabilities that were documented in the first half of 2007, of which seven were medium severity and 18 were low," Symantec added.
No less than 57 security vulnerabilities affected Internet Explorer in 2007, but the volume is lower compared with just the holes that plagued Firefox between July and December of the past year. Furthermore, only 13 security holes were labeled as medium with the remaining five rated as low out of the 18 IE vulnerabilities in the second half of 2007. In the first half of the past year, IE was impacted by 39 vulnerabilities, with 15 medium, and 23 low.
"In the last six months of 2007, 12 vulnerabilities were documented in Opera. Of these, eight were medium severity and four were low. This is fewer than the seven vulnerabilities that affected Opera in the first half of 2007, of which three were considered medium severity and four were low," Symantec said.
According to the Cupertino-based security company, the increase in popularity of both Firefox and Safari has been synonymous with a jump in the number of vulnerabilities discovered. In the second half of the past year, both Safari and Firefox had more security flaws compared to Internet Explorer.
"While fewer vulnerabilities were discovered in Internet Explorer during this period, Mozilla was subject to a sharp increase. The decrease in Internet Explorer vulnerabilities may be due to the focus on security in Internet Explorer 7. The increase in Mozilla vulnerabilities was a by-product of internal and community driven security audits of the browser," Symantec said.

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //