Researchers from Barracuda Labs discovered that the official website of Amnesty International UK, the human rights non-governmental organization, was compromised and set up to serve drive-by downloads to its visitors.
The experts say that the attack on the human rights group may be an attempt to spy on activists.
“The exploit payload possesses properties of targeted malware but is being served by an exploit of a popular, public website,” Paul Royal, a research consultant, wrote.
He claims that many counties try to keep their activists in line, or at least want to know all there is to know about them. In some cases, zero-day exploits and other techniques are utilized to gather information on them, but this may be a more effective approach.
“Of course, a subset of these activists are too smart to click on links in even well-worded spearphishing emails. But what if you compromised a website frequented by these activists (e.g., Amnesty International)? Then your targets come to you. The context-specific damage potential is significant,” Royal added.
So how does the infection chain work?
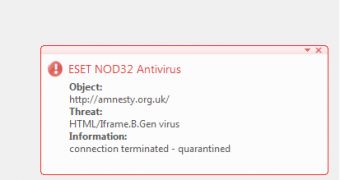
Individuals who visit Amnesty’s UK website (amnesty.org.uk) also load the content of an iframe, strategically placed on the site, which opens a compromised Brazilian automotive site that loads malicious Java content.
In order to succeed in placing the final payload on the targeted device, the exploit relies on a vulnerability in the Java Runtime Environment component in Oracle Java SE JDK and JRE 7 and 6 Update 27 and earlier.
This is what I was talking about yesterday regarding the flaws in Java that are used by cybercriminals to launch their operations. While the specific weakness was patched up in October 2011, it’s very unlikely that most users applied the update.
Amnesty International was notified on the issue by Barracuda, but, unfortunately, nothing has been done so far to remedy the situation. Even more unfortunate is that the pieces of malware served by the site are only detected by one third of the security solutions providers.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //