Yesterday, AMD has officially introduced its first APU that was designed for tablet use, the Z-01, and now the company has revealed additional information about this accelerated processing unit based on the Bobcat CPU core.
The recently uncovered details explain how AMD managed to decrease the power consumption of the APU in order to make it fit for tablet use.
From what we can tell from the slide presented, most of the energy savings were achieved by using lower core and north bridge operating voltages as well as a new local hardware thermal control mode that wasn't previously available in AMD's Ontario chips.
Furthermore, AMD has also reduced the idle operating clocks of both the CPU and the integrated graphics units, as these can now run at 615MHz and 174MHz, respectively.
All these modifications enabled the Sunnyvale company to reduce the TDP of the chip from 9W, in the Ontario C-50, to about 6.4W (yesterday's reports placed the TDP at 5.9W) in the Desna Z-01.
In addition to the new power-saving technologies included, the Z-01 also supports bidirectional Turbo Core, which means that it can increase its base operating frequency when CPU hungry tasks are being run.
Just as its older brother, the C-50, AMD's Desna APU features a pair of Bobcat cores clocked at 1GHz as well as an on-die Radeon HD 6250 graphics core with 80 stream processors.
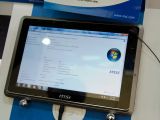
AMD has already started shipping these chips to its hardware partners and the first tablet to use this processor is going to be the MSI Windpad 110W, which is on display right now at Computex.
In addition to the AMD APU, MSI's tablet features a 10-inch touch screen, is designed to run Windows 7 (the demo tablet was running Win7 Pro) and should hit retail for around $599. (via ComputerBase)

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //