Google reveals another mass infection which affected hundreds of thousands of sites that relied on ASP or ASP.NET web application frameworks.
Armorize informed us of the incident, but since the announcement was made, the number of infected websites has doubled, reaching more that 300,000.
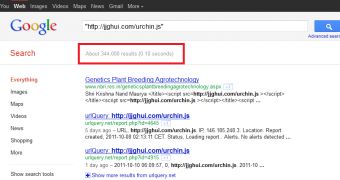
A malicious script that points to "jjghui(dot)com/urchin(dot)js" got injected into the victim locations which the researchers reveal to be targeting English, German, French and other language speakers.
Unfortunately, internauts with outdated browser components get instantly infected when they visit one of the compromised locations, without even realizing what hit them and even though the drive-by download attack seems to be targeting only the websites based on the above mentioned framework, there are plenty of victims to choose from.
At the time Armorize made available the discovery, only 6 of 43 security solution vendors detected the served malware as being a threat.
The malevolent script loads an iframe from www3.strongdefenseiz.in and www2.safetosecurity.rr.nu, both of them hosted in the United States by different vendors, while the address from the script tries to resolve a Russian IP.
After what I've seen, it seems that all sorts of sites were hit, including restaurants, office supply, construction and even genetics companies.
The webmasters of these locations will quickly need to remove the string that starts the chain reaction in order to protect their customers.
Home users who deploy protection measures should be safe as once a few anti-virus vendors learn of a threat, the rest closely follow and quickly blacklist the piece of software that causes harm. Also, if you haven't done it yet, be sure to quickly update your browser and all of its components such as Adobe Flash and Java, as in most cases, the vulnerabilities present in the older versions are exploited by attackers to serve these multiple browser-based drive-by download exploits.
 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //