A recent report released by Imperva shows that the healthcare sector and sites hosted on WordPress were the favorite targets of attacks during the past year.
The Imperva Web Application Attack Report includes statistics from the analysis of 297.954 attacks, 22,850,023 alerts on 198 applications.
The data highlights that each application was attacked by at least 75% of all the possible attack types, showing that hackers have had a diversified portfolio at their disposal during the past year.
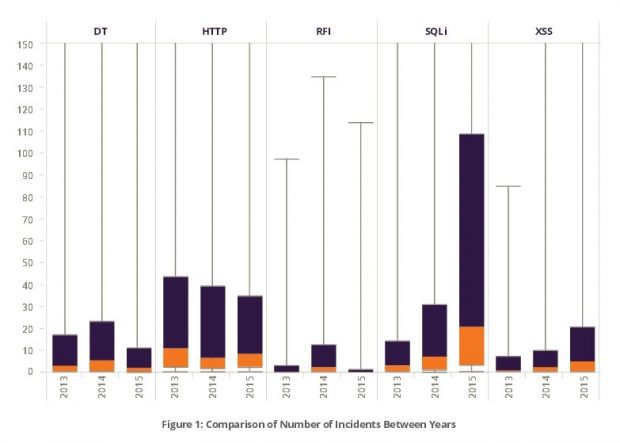
XSS and SQLi have seen the biggest growth in 2015
Out of all the attack types, XSS (cross-site scripting) and SQLi (SQL injection) saw the biggest rise compared to last year. SQLi attacks grew 3 times compared to last year, while SQLi, 2.5 times.
While the data-rich records from the healthcare industry were the most sought after, mainly due to their high value on the black market, most attackers weren't that focused.
The report also shows that, during 2015, there was a large number of blind Shellshock attacks across the Web, with hackers randomly looking for a way to penetrate applications.
WordPress, everyone's favorite CMS
Besides healthcare, attackers also displayed a taste for WordPress-powered sites. This may have something to do with the large target area these sites present, currently WordPress having a 25% market share across all sites on the Internet, and 50% market share among CMSs.
During 2015, sites hosted on WordPress faced 250 times more attacks than non-CMS sites, but also received 7 times more spam than non-CMS sites. Another attack that saw a major increase for WordPress sites compared to last year was RFI (remote file inclusion), also growing 7 times.
But attacks on CMS sites, in general, were up, occurring 3 times more often than on non-CMS sites. Compared to last year, Drupal, Joomla, Magento, and Blogger all saw an increase in hacking activity. The favorite attack vector for attackers was RCE (remote code execution), which was used for 31% in all attacks on CMSs, 41% in all attacks on non-CMSs, 48% on WordPress, 53% on non-WordPress, 35% on PHP Web apps, and 45% on non-PHP.

 14 DAY TRIAL //
14 DAY TRIAL //